-
January 10, 2014
Mini-project: Hitch receiver bike rack stand
Living in a studio apartment, storage space can be hard to come by. To have a place to store both my bike and hitch receiver bike rack, I designed and built a rolling stand that holds the rack upright, also serving as a nice work stand.
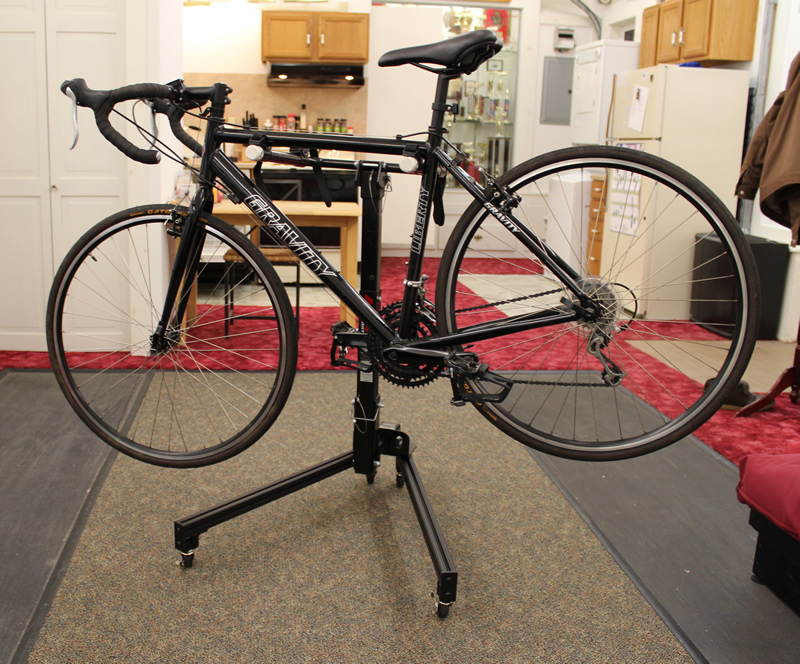

Completed stand with bike. The frame is made from 80/20 t-slot extrusions and hardware, which are available at Amazon.com. On top is a 2 inch Reese hitch receiver, and below is a set of swivel casters, two of which are locking. One nice feature of this design is that it only requires cutting and tapping—no welding, drilling, or more complicated machining necessary before it’s ready for assembly.
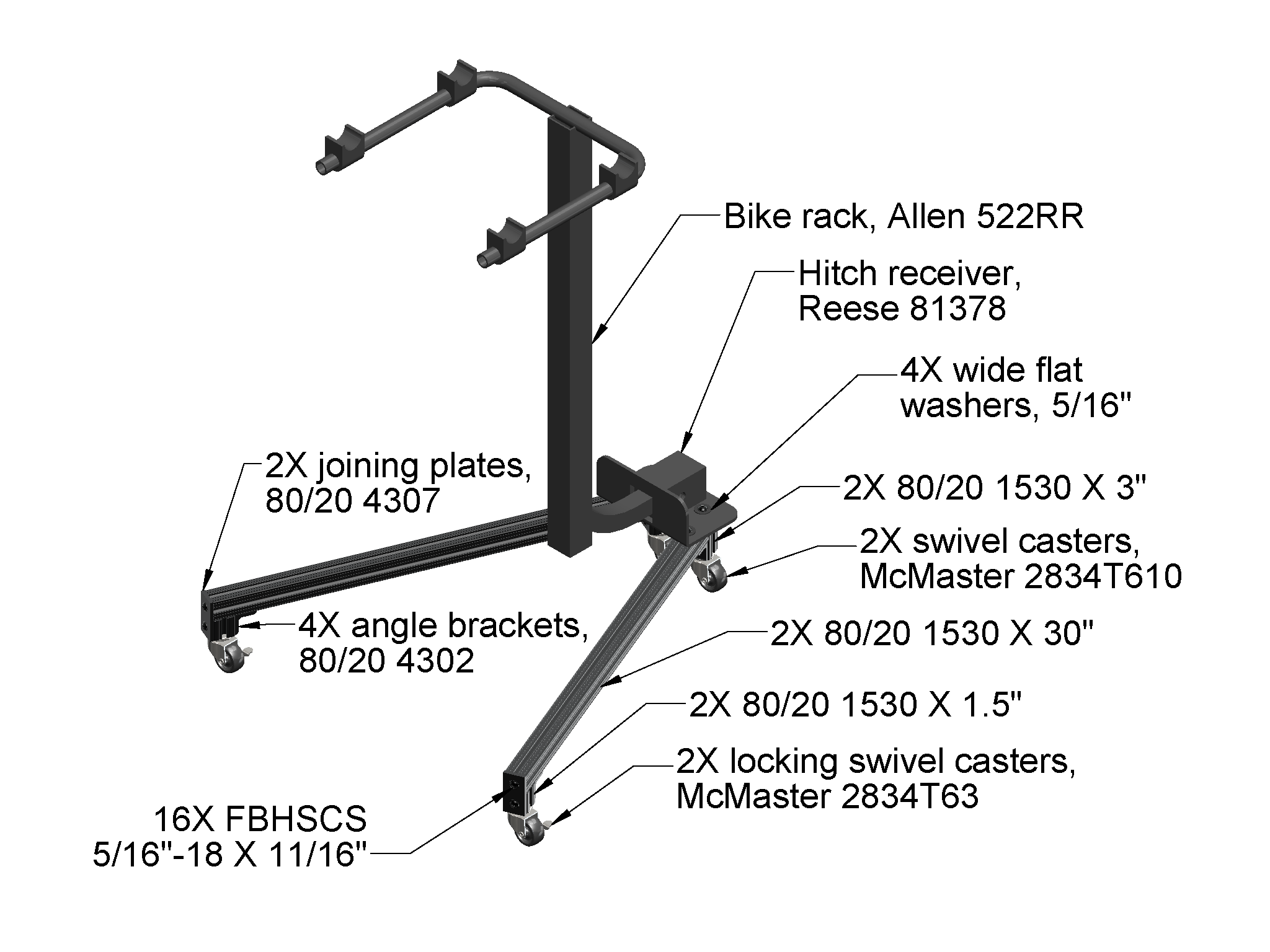
Bike rack stand design. The SolidWorks 2012 CAD models for this assembly can be downloaded here.
-
January 07, 2014
Improving IPython Notebook integration with Windows
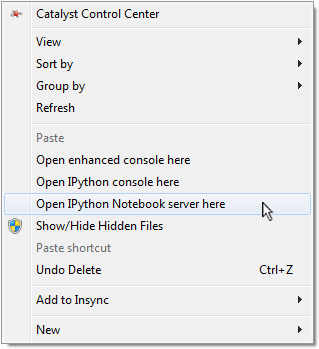
By default, the awesomely useful and fun IPython Notebook does not integrate with Windows so seamlessly. A console and then the notebook server must be opened in the proper directory in order to open a new or existing notebook. These extra steps make the IPython Notebook slightly less ideal for quickly jotting down ideas—one of its greatest uses!
Not to fear, however, as the Windows Registry can easily be modified to
- Open notebooks directly from Windows Explorer.
- Create a shortcut to launch the IPython Notebook server within the current directory.
Simply download and run ipython.reg to add the entries shown below to your registry automatically.
These entries were put together from instructions located here. A similar solution can also be found here.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\Background\shell\ipynb] @="Open IPython Notebook server here" [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\Background\shell\ipynb\command] @="\"C:\\Python27\\Scripts\\ipython.exe\" \"notebook\" \"%V\"" [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\ipynb] @="Open IPython Notebook server here" [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Directory\shell\ipynb\command] @="\"C:\\Python27\\Scripts\\ipython.exe\" \"notebook\" \"%V\"" [HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\ipynb_auto_file\shell\open\command] @="\"C:\\Python27\\Scripts\\ipython.exe\" \"notebook\" \"%1\""